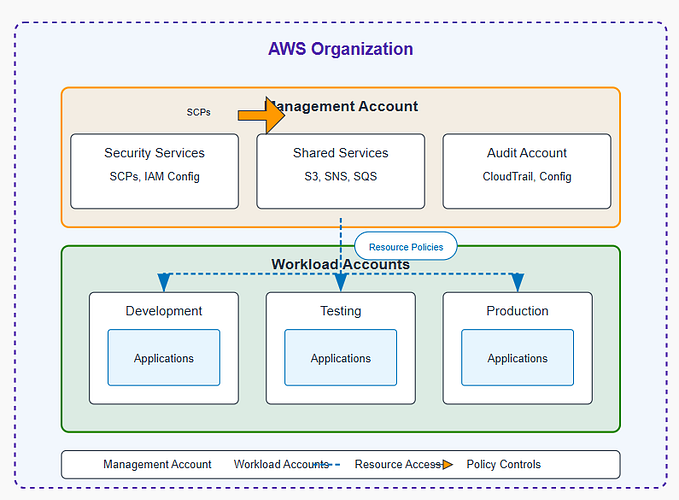
Project-Specific AWS Configuration

To define AWS configure settings specifically for a project in its folder, you can use environment variables or a local AWS configuration file.
Here’s a simple way to do it…
Environment Variables
You can set environment variables for your AWS credentials. These will override the global settings in your ~/.aws/ directory.
In your project folder, create a script (e.g., setenv.sh) with the following content:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=your_access_key
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=your_secret_key
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=your_preferred_regionThen, run the script in your terminal to set these variables:
source setenv.shThis approach is good for a temporary change in a single terminal session.
Local AWS Config File
You can create a local .aws folder inside your project directory with its own config and credentials files.
- Create a .aws folder in your project directory.
- Inside this folder, create two files: config and credentials.
- Add your configurations in these files.
For config:
[default]
region=your_preferred_region
output=jsonFor credentials:
[default]
aws_access_key_id=your_access_key
aws_secret_access_key=your_secret_keyYou’ll then need to set the AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE and AWS_CONFIG_FILE environment variables to point to these files.
In setenv.sh:
export AWS_SHARED_CREDENTIALS_FILE=$(pwd)/.aws/credentials
export AWS_CONFIG_FILE=$(pwd)/.aws/configRemember, you should never commit AWS credentials to source control.
If you’re using a local AWS config, make sure to add .aws/ to your .gitignore file to avoid accidentally pushing it.